The Role and Impact of Big Data in Finance
What is Big Data?
Big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that require advanced computational tools and techniques for analysis. This data can reveal intricate patterns, trends, and associations, particularly those related to human behavior and interactions. The defining characteristics of big data are encapsulated in what is commonly known as the “Three Vs”:
- Volume: This denotes the massive amount of data generated every second, ranging from terabytes to petabytes. It’s not just the quantity but also the density and complexity of the data that matter.
- Velocity: This refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed. Big data systems must be capable of handling real-time or near-real-time data streams to remain relevant.
- Variety: Big data comes in various formats, including structured data (like databases), unstructured data (like social media posts), and semi-structured data (like web logs). This diversity necessitates sophisticated methods for data integration and analysis.
Big data analytics provides insights that can significantly enhance decision-making processes, from designing personalized services to identifying emerging trends. It enables businesses to harness the power of data for strategic benefits, thus transforming their operations and competitive standing.
Benefits of Using Big Data in Finance
The financial sector is increasingly leveraging big data to gain a competitive edge, optimize operations, and improve customer service. Here are some of the top benefits:
- Improved Decision-Making: Big data analytics tools process extensive datasets from various sources such as market data, customer transactions, and social media. This comprehensive analysis uncovers hidden trends and patterns, leading to more informed and strategic decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: Automation of tasks like compliance checks, fraud detection, and risk management is possible with big data. By focusing on profitable areas and optimizing resource allocation, financial institutions can significantly cut operational costs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Big data allows financial institutions to understand customer preferences and behaviors better, leading to more personalized services. Tailored product recommendations and improved customer interactions can increase satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: By identifying inefficiencies and automating processes, big data helps financial institutions optimize their operations. For example, it aids in refining trading strategies and improving asset management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with financial regulations can be streamlined using big data. Automated reporting and transaction tracking help institutions maintain adherence to regulations and manage audits more effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: Big data analytics equips financial institutions with insights into market trends and risk factors, allowing them to make better investment decisions and gain a competitive edge over peers.
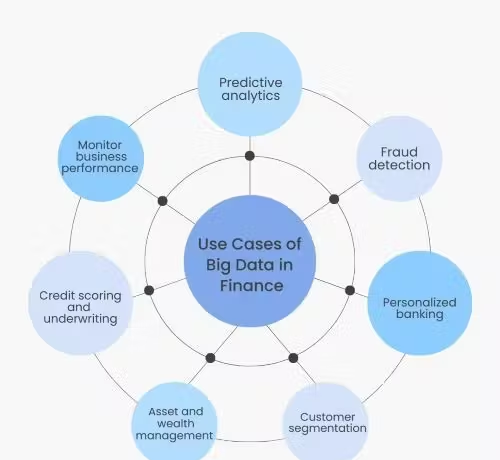
Use Cases of Big Data in Finance
The application of big data in finance is vast, with several key use cases:
- Predictive Analysis: Utilizing historical and real-time data, financial institutions can forecast future trends, risks, and opportunities. For instance, predictive models help assess credit risks and investment opportunities.
- Fraud Detection: Big data enhances fraud detection capabilities by analyzing transaction patterns and identifying anomalies. Machine learning algorithms can spot fraudulent activities like identity theft and money laundering.
- Customer Segmentation: Analyzing financial behavior and preferences allows institutions to segment customers into distinct groups. This segmentation facilitates targeted marketing and personalized service offerings.
- Personalized Banking: Big data enables financial institutions to offer tailored banking services based on individual customer needs and preferences, enhancing satisfaction and loyalty.
- Asset and Wealth Management: Investment firms use big data to analyze market trends and economic indicators, improving decision-making and portfolio management.
- Credit Scoring and Underwriting: Big data enhances credit scoring by incorporating a broader range of data sources, leading to more accurate assessments and reduced loan default rates.
- Business Performance Monitoring: Financial institutions use big data to track key financial metrics and compare performance against industry benchmarks, leading to more informed strategic planning.
Challenges of Big Data in Finance
Despite its advantages, big data presents several challenges:
- Data Security and Privacy: The financial sector is a prime target for cyberattacks. Ensuring data security and privacy while leveraging big data requires robust protection measures and compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data privacy laws and regulations while managing large volumes of data can be challenging. Financial institutions must ensure their data practices align with regulatory requirements.
- Data Silos: Large financial institutions often have data stored in various systems, making it difficult to access and analyze. Integrating these disparate data sources is crucial for effective big data analytics.
Real-World Examples of Big Data in Finance
- JP Morgan & Chase: Uses big data for predictive analytics to forecast market risks and opportunities. Their systems analyze customer transactions and economic data to optimize cash forecasting and detect market trends.
- Goldman Sachs: Employs big data for investment analysis and risk management. Their models process structured and unstructured data, enhancing their investment strategies and decision-making processes.
- American Express: Utilizes big data for fraud detection, processing transaction data in real time to identify and prevent fraudulent activities. Their Enhanced Authorization tool helps in verifying transactions and reducing fraud.
- BlackRock: Leverages big data to improve asset management and investment strategies. By analyzing vast datasets, BlackRock identifies investment opportunities and manages portfolio risks effectively.
- Wells Fargo & Company: Uses big data for customer segmentation and personalization. Their analytics team integrates data from various sources to enhance customer experiences and optimize business operations.
- Morgan Stanley: Applies big data for portfolio analysis and fraud detection. Their investment in data technologies helps them make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
- Societe Generale: Focuses on big data and AI to enhance investment decisions and client services. Their use of data analytics supports real-time risk monitoring and personalized financial products.
Conclusion
Big data has revolutionized the finance industry by providing deep insights and enhancing decision-making processes. Financial institutions are leveraging big data to improve operational efficiency, customer experiences, and regulatory compliance. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for big data in finance will only grow, offering new opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage.
For organizations looking to harness the full potential of big data, partnering with expert providers like Turing can be a game-changer. Turing offers tailored big data services that optimize operations, enhance risk management, and support strategic decision-making. Join the ranks of Fortune 500 companies and emerging startups that have successfully leveraged Turing for their big data needs.